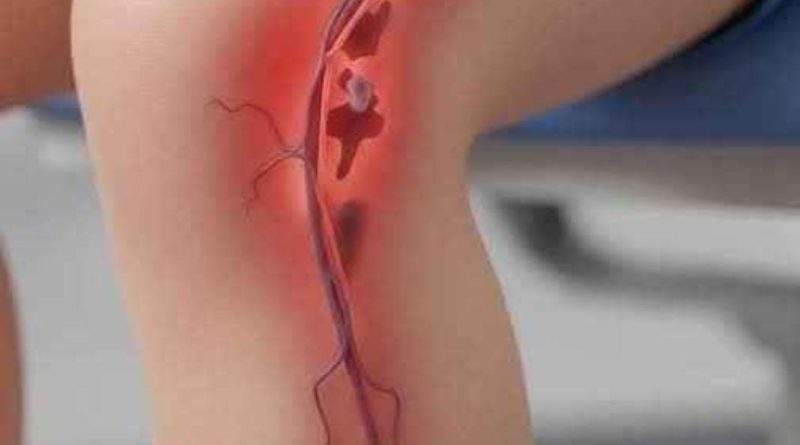
What is Venous Thrombosis? Causes and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Venous thrombosis is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot, also known as a thrombus, forms inside a vein and obstructs normal blood flow. This blockage can be partial or complete and may develop without obvious warning signs. Because it often progresses silently, venous thrombosis can become life threatening if it is not diagnosed and treated early.
Venous thrombosis can occur in different parts of the body, but it most commonly affects the deep veins of the legs. When this happens, it is referred to as deep vein thrombosis, or DVT. The condition is dangerous not only because it restricts circulation, but also because the clot can break loose and travel through the bloodstream.
What Happens During Venous Thrombosis
When a clot forms inside a vein, blood is no longer able to circulate normally. This leads to increased pressure in the affected area and can damage surrounding tissues. In more severe cases, part of the clot can detach and move to the lungs. This causes a pulmonary embolism, which blocks blood flow in the lungs and is considered a medical emergency that can be fatal without immediate treatment.
Main Causes of Venous Thrombosis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing venous thrombosis. One of the most common causes is prolonged immobility. Long flights, extended car travel, hospitalization, or bed rest can slow blood flow in the legs and promote clot formation.
Surgery and trauma are also major risk factors. Orthopedic surgeries such as hip or knee replacements, as well as fractures and serious injuries, significantly increase the likelihood of developing blood clots.
Some individuals have inherited coagulation disorders. These genetic conditions cause the blood to clot more easily than normal, sometimes even without a clear trigger.
Hormonal changes play an important role as well. Pregnancy, hormone replacement therapy, and the use of oral contraceptives can alter the body’s clotting mechanisms and increase the risk of thrombosis.
Cancer and its treatments are another significant factor. Tumors, chemotherapy, and certain medications can interfere with normal blood coagulation.
Lifestyle factors such as obesity and smoking also contribute. Both impair circulation, increase blood viscosity, and place additional strain on the vascular system.
Warning Signs You Should Not Ignore
Venous thrombosis can develop without symptoms, which makes awareness especially important. When symptoms do appear, they usually affect one leg and may include swelling, particularly in the calf, pain or tenderness when touched, warmth or a burning sensation in the affected area, changes in skin color such as redness or a bluish tint, and visible or enlarged veins. If any of these symptoms occur, medical attention should be sought immediately.
How to Reduce Your Risk
Preventive measures can significantly lower the risk of venous thrombosis. Avoid sitting or lying down for long periods without movement. If you travel or work at a desk, stand up and walk regularly. Staying well hydrated supports healthy blood flow. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding smoking are also important steps. Individuals with a family history of thrombosis or those considering hormonal treatments should consult a healthcare professional. Compression stockings may be recommended for people at higher risk or after surgery.
Conclusion
Venous thrombosis is often silent, but its consequences can be severe and even fatal. Understanding its causes, recognizing warning signs, and adopting preventive habits can make a critical difference. Paying attention to your body and seeking medical care early can truly save your life.