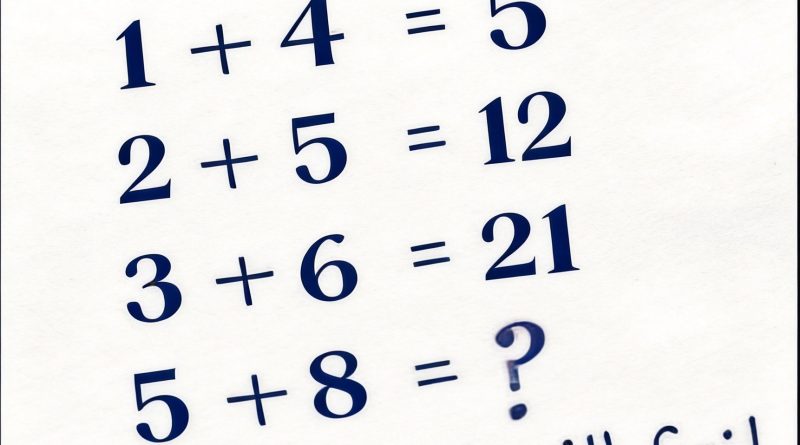Internet Users Can’t Agree on the Answer to This Math Problem
If you’re like many people, the days of sitting in a classroom and solving endless math problems feel like a distant memory.
For some, numbers and formulas evoke a sense of curiosity and enjoyment, while for others, the mere mention of arithmetic can cause anxiety or boredom.
Yet, despite decades of moving away from traditional math exercises, the internet has created a new space for people to engage with numbers — in the form of brain teasers, puzzles, and logic challenges.
What’s remarkable is how these puzzles, often deceptively simple in appearance, can capture our attention for hours, igniting debate and discussion across forums, social media platforms, and online communities.

One of the most talked-about math puzzles in recent months has been the seemingly simple sequence:
1 + 4 = 5
2 + 5 = 12
3 + 6 = 21
5 + 8 = ?
At first glance, it looks like a basic arithmetic problem — straightforward addition that even a beginner might be able to solve. But the puzzle quickly becomes puzzling the moment you try to apply conventional rules of addition.
The results clearly don’t match standard arithmetic: 2 + 5 certainly does not equal 12, and 3 + 6 is not 21. This discrepancy is what makes the puzzle so intriguing.
It requires the solver to step outside the realm of normal addition and look for patterns, relationships, or hidden rules.
Why This Puzzle Captures Attention
This puzzle is a classic example of what mathematicians and educators call a “pattern problem” or “sequence puzzle.” The challenge doesn’t lie in performing arithmetic correctly, but in recognizing the underlying rule that governs the transformations.
These types of puzzles appeal to a wide audience because they combine logic, creativity, and reasoning skills — attributes that extend beyond pure mathematics.
The popularity of this puzzle is evident across online platforms like Reddit, Quora, and various brain-teaser websites, where thousands of users have attempted to solve it.
Some approach it analytically, testing different mathematical operations like multiplication, division, or factorials. Others take a more creative route, interpreting the “+” sign not as addition but as a signal for a sequence-based rule or cumulative operation.
This diversity of approaches explains why so many different answers appear online, each with its own justification.
Exploring Different Approaches

To understand why this puzzle is so divisive, let’s examine some of the most common interpretations:
1. The Cumulative Sum Method
One popular method involves building on previous results. Here, the pattern is understood as:
Result = A + (B × previous result)
Applying this rule step by step:
-
1 + 4 = 5
Since there is no previous result, we simply take the first line as given. -
2 + 5 = ?
Multiply 5 (B) by the previous result (5 from the first equation): 5 × 5 = 25.
Add 2 (A): 25 + 2 = 27. -
3 + 6 = ?
Multiply 6 (B) by the previous result (27 from the second equation): 6 × 27 = 162.
Add 3 (A): 162 + 3 = 165. -
5 + 8 = ?
Multiply 8 (B) by the previous result (165): 8 × 165 = 1320.
Add 5 (A): 1320 + 5 = 1325.
This method produces a sequence that grows rapidly, and while it may seem extreme, it highlights how a single change in rule interpretation can drastically affect the outcome. It also demonstrates that these puzzles test flexibility of thinking more than basic arithmetic.

2. The “Add and Multiply” Rule
Another approach interprets the problem as:
Result = (A × B) + A
Step by step:
-
1 + 4 = (1 × 4) + 1 = 4 + 1 = 5 ✅
-
2 + 5 = (2 × 5) + 2 = 10 + 2 = 12 ✅
-
3 + 6 = (3 × 6) + 3 = 18 + 3 = 21 ✅
-
5 + 8 = (5 × 8) + 5 = 40 + 5 = 45 ✅
This method is perhaps the most widely cited “correct” answer for those approaching the puzzle with a clean mathematical formula.
It explains the pattern in a logical, repeatable way and produces results consistent with the first three lines. For many puzzle enthusiasts, this solution is both satisfying and elegant because it balances simplicity and creativity.
3. Adding the Previous Result
A third approach interprets the puzzle as adding the previous result to the next sum: